Epigenetics
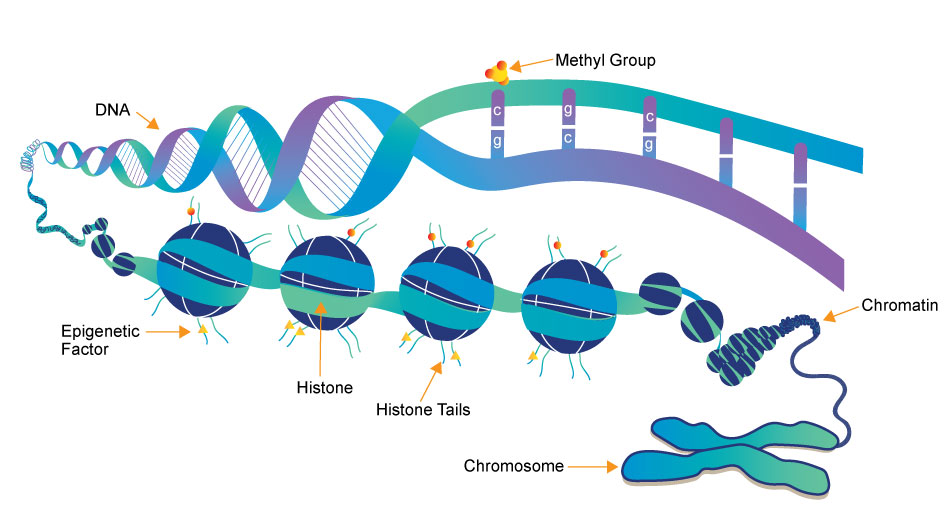

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
EZH2 抑制剂
PF-06726304 是一种强效的、与SAM(S-腺苷甲硫氨酸)竞争的 EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2) 赖氨酸甲基转移酶抑制剂。 -
JAK1 and TYK2 抑制剂
PF-06700841 是一种 JAK1 和 TYK2 激酶的抑制剂。CAS: 1883299-62-4(游离碱) -
BET 抑制剂
Mivebresib,也被称为 ABBV-075,是一种强效的 BET 抑制剂(含 BRD(bromodomain)的蛋白质),具有潜在的抗肿瘤活性。 -
JAK3/2/1 抑制剂
托法替尼是一种可口服的 JAK3/2/1 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 1, 20 和 112 nM。- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
-
HDAC 抑制剂
Valproic acid 是一种 HDAC 抑制剂,其 IC50 在 0.5 至 2 mM 范围内,同时抑制 HDAC1(IC50,400 μM),并诱导 HDAC2 的蛋白酶体降解;Valproic acid sodium salt 用于治疗癫痫、双相情感障碍以及预防偏头痛。- Dan Zhao, .et al. , Poult Sci, 2022, Mar; 101(3): 101642 PMID: 35016046
-
HDAC 抑制剂
Tucidinostat 是一种有效的、可口服的 HDAC酶 类 I(HDAC1/2/3)和类 IIb(HDAC10)抑制剂,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为95、160、67和78 nM,对 HDAC8 和 HDAC11 的活性较低(IC50分别为733 nM和432 nM),对 HDAC4/5/6/7/9 无影响。 -
PTP 抑制剂
Sodium stibogluconate(Stibogluconate trisodium nonahydrate)是一种强效的蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶抑制剂。Sodium stibogluconate在10, 100, 100 微克/毫升的浓度下分别抑制99%的SHP-1、SHP-2和PTP1B活性。 -
PARP 抑制剂
Rucaparib Camsylate 是一种 PARP 抑制剂,其对 PARP1 的 Ki 值为 1.4 nM,并且还显示出对其他八个 PARP 域的结合亲和力。 -
PARP1 and PARP2 抑制剂
Niraparib hydrochloride (MK-4827 hydrochloride) 是一种高效且可口服吸收的 PARP1 和 PARP2 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 3.8 nM 和 2.1 nM。 -
JAK1 抑制剂
Upadacitinib (ABT-494) 是一种强效且选择性的 Janus 激酶(JAK)1 抑制剂,正在开发中,用于治疗多种自身免疫性疾病,其半抑制浓度(IC50)为 43 nM。IC50 & 目标:IC50:43 nM(JAK1),200 nM(JAK2) -
JAK1 抑制剂
Abrocitinib (PF-04965842) 是一种强效的、口服活性的、选择性 JAK1 抑制剂,其对 JAK1 和 JAK2 的 IC50 分别为 29 nM 和 803 nM。Abrocitinib (PF-04965842) 对 TYK2 的活性较低(IC50 为 1.253 μM),并在刺激后抑制 STAT1、STAT3 和 STAT5 的磷酸化。在自身免疫疾病中有效。 -
HDAC 抑制剂
EDO-S101 是一种广谱 HDAC 抑制剂;分别对 HDAC1、HDAC2 和 HDAC3 的抑制作用的 IC50 值为 9 nM、9 nM 和 25 nM。 -
PARP14 抑制剂
PARP14 抑制剂 H10,化合物 H 10,是一种针对 PARP14 的选择性抑制剂(IC50=490 nM),相较于其他 PARP 抑制效果高出 24 倍以上(??24 倍以上 PARP1)。PARP14 抑制剂 H10 诱导 caspase-3/7 介导的细胞凋亡。 -
SUV39H2 抑制剂
OTS186935 是一种蛋白质甲基转移酶 SUV39H2 抑制剂,其 IC50 为 6.49 nM。- Jennings Luu, .et al. , Hum Mol Genet, 2020, Jul 21;ddaa158 PMID: 32691052