Epigenetics
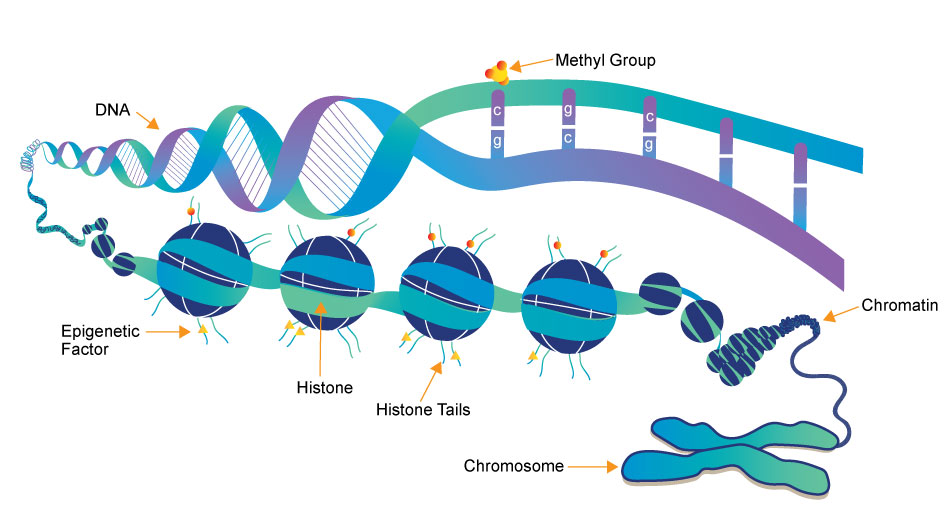

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
Aurora A/B Kinase 抑制剂
PF-03814735 是一种新型、高效、可逆的 Aurora A/B 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 0.8 nM/5 nM,对 Flt3、FAK、TrkA 的抑制作用较弱,对 Met 和 FGFR1 几乎无活性。目前处于第一阶段临床试验。 -
FAK 抑制剂
PF-562271 是一种口服生物利用度高的小分子,具有潜在的抗肿瘤和抗血管生成活性,是一种 ATP竞争性粘着斑激酶(FAK)抑制剂。- Jiping Yue, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11692 PMID: 27216888
-
FAK 抑制剂
PF 573228 是一种强效且选择性的焦点粘附激酶 (FAK) 抑制剂(IC50 = 4 nM)。- Dagyeong Lee, .et al. , J Transl Med, 2024, Feb 14;22(1):154 PMID: 38355577
- Izumi D, .et al. , Int J Cancer, 2016, Mar 1;138(5):1207-19 PMID: 26414794
- Aya Yokota-Nakatsuma, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 37914 PMID: 27897208
-
FAK 抑制剂
NVP-TAE226 是一种强效的 FAK 抑制剂,IC50 为 5.5 nM,对 Pyk2 也有适度的抑制作用(IC50=3.5 nM);对 InsR、IGF-1R、ALK 和 c-Met 的抑制作用较弱,低 10 到 100 倍。- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
-
FAK 抑制剂
PF-04554878 是一种新型的 FAK激酶抑制剂,能够减缓胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤细胞的生长并诱导凋亡。- Shalana O'Brien, .et al. , Oncotarget., 2014, Sep; 5(17): 7945-7959 PMID: 25277206
-
FAK 抑制剂
PF-00562271 是 PF-562271 的苯磺酸盐,它是一种强效的、与ATP竞争的、可逆的FAK和Pyk2抑制剂,其IC50分别为1.5 nM和14 nM。- Dai Sonoda, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2022, Jan;47(1):19 PMID: 34796907
-
multi-kinase 抑制剂
Conteltinib (CT-707) 是一种多激酶抑制剂,针对 FAK、ALK 和 Pyk2。Conteltinib (CT-707) 对 FAK 有显著的抑制作用,其 IC50 为 1.6 nM。 -
FAK 抑制剂
Defactinib hydrochloride(VS-6063 hydrochloride;PF 04554878 hydrochloride)是一种新型的FAK抑制剂,它能够以时间和剂量依赖的方式抑制FAK在Tyr397位点的磷酸化。 -
FAK and Pyk2 kinase 抑制剂
PF-562271 hydrochloride 是一种强效的、ATP竞争性的、可逆的 FAK 和 Pyk2 激酶抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 1.5 nM 和 13 nM。