Epigenetics
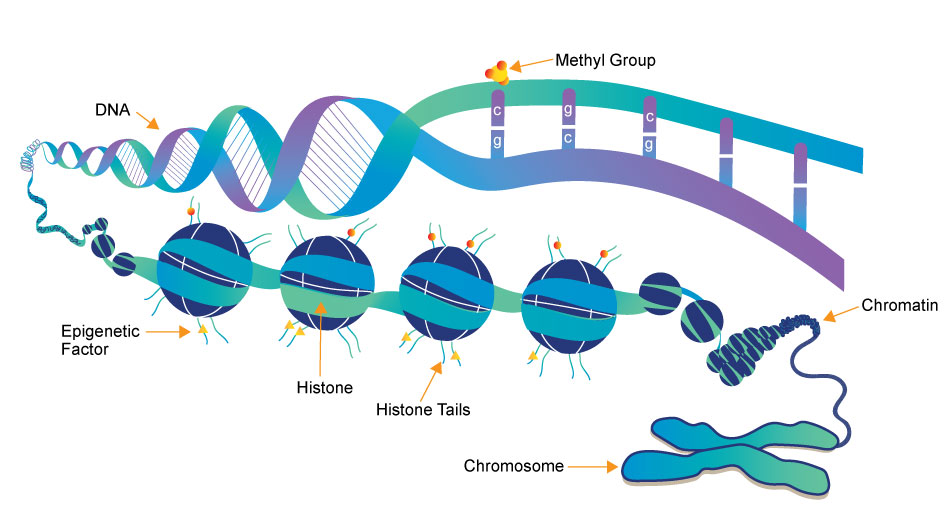

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
SMYD2 抑制剂
SMYD2-IN-1 是一种从专利 WO2016166186A1 中提取的 SMYD2 抑制剂,化合物示例 1.1,具有 4.45 nM 的 IC50。 -
Sirt2 degrader
PROTAC Sirt2 Degrader-1 是基于 SirReal 的 PROTAC,作为 Sirt2 降解剂,由高效且同型选择性的 Sirt2 抑制剂、连接体和真正的 cereblon 配体组成,用于 E3 泛素连接酶。 -
BET degrader
PROTAC BET Degrader-1 是一种基于 PROTAC 的强效 BET 降解剂,能在低浓度下降低 BRD2、BRD3 和 BRD4 蛋白水平。 -
PROTAC BRD9 degrader
PROTAC BRD9 Degrader-1 是一种领先的 PROTAC BRD9 化学降解剂(IC50=13.5 nM),可作为选择性探针用于研究 BAF 复合体 生物学。 -
EHMT 抑制剂
EHMT2-IN-1 是一种强效的 EHMT 抑制剂,对 EHMT1 肽、EHMT2 肽和细胞内 EHMT2 的 IC50 均小于 100 nM。用于血液疾病或癌症的研究。 -
Sirt2 抑制剂
SirReal1-O-propargyl 是一种选择性且高效的Sirtuin 2 (Sirt2)抑制剂,其IC50为2.4 μM。 -
BRD4 抑制剂
ZL0420 是一种强效且选择性的含溴结构域蛋白4(BRD4)抑制剂,其对 BRD4 BD1 的 IC50 值为 27 nM,对 BRD4 BD2 的 IC50 值为 32 nM。 -
Dot1L 抑制剂
Dot1L-IN-2 是一种强效、选择性且可口服的 Dot1L (一种组蛋白甲基转移酶) 抑制剂,其 IC50 和 Ki 分别为 0.4 nM 和 0.08 nM。 -
PARP1/2 抑制剂
Talazoparib tosylate (BMN 673ts) 是一种新型、高效且可口服的 PARP1/2 抑制剂,其对 PARP1 的 IC50 为 0.57 nM。- Majid Momeny, .et al. , EMBO Mol Med, 2024, Jun 17 PMID: 38886591
-
MATA2 抑制剂s
AGI-25696 是一种甲硫氨酸腺苷转移酶 2A(MATA2)抑制剂,可用于治疗癌症。AGI-25696 在体内阻断 MTAP 缺失肿瘤的生长。- Jennifer Kim, .et al. , Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2022, Mar 18;10:855755 PMID: 35372313
-
pan HDAC 抑制剂
Tefinostat(CHR-2845)是一种针对单核细胞/巨噬细胞的全面HDAC抑制剂,通过细胞内酯酶人类羧酸酯酶-1(hCE-1)被裂解成活性酸CHR-2847。具有抗单核细胞系列白血病活性。 -
KDM5 抑制剂
KDM5A-IN-1 是一种效力强大的、口服生物利用度高的全组蛋白赖氨酸去甲基化酶5(KDM5)抑制剂,其对 KDM5A、KDM5B 和 KDM5C 的 IC50 分别为 45 nM、56 nM 和 55 nM,对 PC9 H3K4Me3 的 EC50 值为 960 nM。 -
PPI 抑制剂
BRCA1-IN-2(化合物15)是一种细胞渗透性的蛋白-蛋白相互作用(PPI)抑制剂,针对BRCA1,具有 IC50 为0.31 μM和 Kd 为0.3 μM,通过破坏BRCA1 (BRCT)2/蛋白相互作用显示出抗肿瘤活性。 -
BRD4 抑制剂
JQ-1 羧酸是一种高效、选择性且能渗透细胞的 BRD4 抑制剂,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为 BRD4(1) 的 77 nM 和 BRD4(2) 的 33 nM。- Rahel Fitzel, .et al. , Neoplasia, 2023, Jul;41:100902 PMID: 37148657