Epigenetics
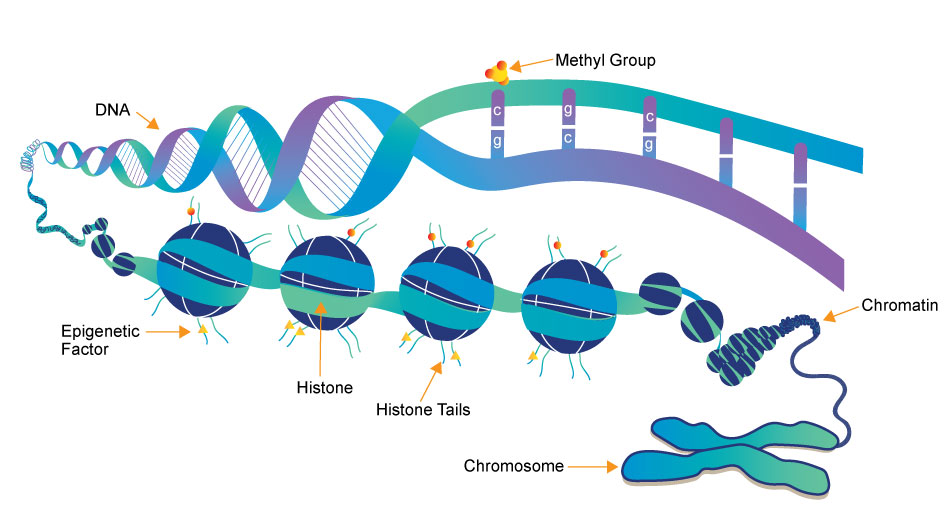

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
Mdm2 拮抗剂
MDM2拮抗剂nutlin-3是一种强效的凋亡诱导剂。- Maxime Parisotto, .et al. , J Exp Med, 2018, Jun 4; 215(6): 1749-1763 PMID: 29743291
- Ohmuro-Matsuyama Y, .et al. , Anal Biochem, 2018, Dec 15;563:61-66 PMID: 30316750
- Alisa A. Garaeva, .et al. , Cell Cycle, 2016, 15(1): 64-71 PMID: 26771712
- A G Evstafieva, .et al. , Cell Death Dis., 2014, 5(11): e1511. PMID: 25375376
-
MDMX 抑制剂
NSC207895 是一种细胞渗透性的苯并呋喃化合物,它通过抑制 MDMX 启动子的转录活性(在 HT1080 细胞中的 IC50 = 2.5 微摩尔),在 MCF-7、LNCaP 和 A549 细胞中(1 到 10 微摩尔,持续 16 到 24 小时)降低 p53 负调控因子 MDMX 蛋白的水平,从而增强 p53 的稳定性和激活。 -
MDM2 抑制剂
Nutlin 3a 是一种强效的 MDM2 (mouse double minute 2) 抑制剂,它能阻止 MDM2 与 p53 的结合,从而诱导 p53 调控基因的表达,并在表达功能性 p53 的细胞中显示出强大的抗增殖活性。- Sho Watanabe, .et al. , J Crohns Colitis, 2021, Feb 17 PMID: 33596306
- Shun Zhang, .et al. , BPB Reports, 2019, 2, 130-133
- Momoko Ishimine, .et al. , Dis Markers, 2018, 2018: 5280736 PMID: 29651325
-
Mdm2 抑制剂
MI-773 是一种新型小分子抑制剂,用于抑制 MDM2-p53 互作,它与 MDM2 高亲和力结合(Ki=0.88 nM),阻断 p53-MDM2 互作。 -
p53-MDM2 interaction 抑制剂
p53 和 MDM2 蛋白相互作用抑制剂手性是一种抑制 p53 和 MDM2 蛋白之间相互作用的抑制剂。 -
p53-MDM2 interaction 抑制剂
p53 和 MDM2 蛋白相互作用抑制剂(外消旋体)是一种抑制 p53 和 MDM2 蛋白之间相互作用的抑制剂。 -
MDMX 抑制剂
SJ 172550 是首个 MDMX 抑制剂,具有 0.84 uM 的 EC50;可逆性结合到 MDMX 上,并有效杀死 MDMX 表达增强的视网膜母细胞瘤细胞。- Saketh S Dinavahi, .et al. , Cancer Immunol Res, 2022, Jun 3;10(6):757-769 PMID: 35439317
-
MDM2 degrader
MD-224 是一种基于蛋白质降解靶向嵌合体(PROTAC)概念的首创类和高效的小分子人类鼠双分钟2(MDM2)降解剂。MD-224 有潜力成为一种新类别的抗癌药物。- Lingling Chen, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, Nov 29:232:116688 PMID: 39617210
-
MDM2 抑制剂
PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-4 是基于 PROTAC 技术的 MDM2 降解剂。PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-4 包含一种强效的 MDM2 抑制剂、连接体和 E3 泛素连接酶 的 MDM2 配体。 -
MDM2 degrader
PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-3 是基于 PROTAC 技术的 MDM2 降解剂。PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-3 由强效的 MDM2 抑制剂、连接器和 E3 泛素连接酶 的 MDM2 配体组成。 -
MDM2 抑制剂
PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-2 是基于 PROTAC 技术的 MDM2 降解剂。PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-2 包含一个强效的 MDM2 抑制剂、连接体和 E3 泛素连接酶 的 MDM2 配体。 -
MDM2 degrader
PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-1 是基于 PROTAC 技术的 MDM2 降解剂。PROTAC MDM2 Degrader-1 包含一个强效的 MDM2 抑制剂、连接体和 E3 泛素连接酶 的 MDM2 配体。 -
Nutlin 3-based MDM2 ligand
Nutlin carboxylic acid (MDM2 ligand 1) 是基于 Nutlin 3 的 MDM2 配体。Nutlin carboxylic acid (MDM2 ligand 1) 可以通过连接器与蛋白质配体连接,形成 PROTACs。 -
Nutlin 3-based MDM2 ligand
(4R,5S)-nutlin carboxylic acid (MDM2 ligand 2) 是基于 Nutlin 3 的 MDM2 配体。 (4R,5S)-nutlin carboxylic acid 可以通过连接器与蛋白质配体连接,形成 PROTACs。 -
HIF-1α 抑制剂
盐酸米诺环素是一种广谱四环素类抗生素,其作用机制是通过结合到细菌的30S核糖体亚基并抑制蛋白质合成。- Viktoria Lazar, .et al. , Nature, 2022, 610: 540-546 PMID: 36198788