Epigenetics
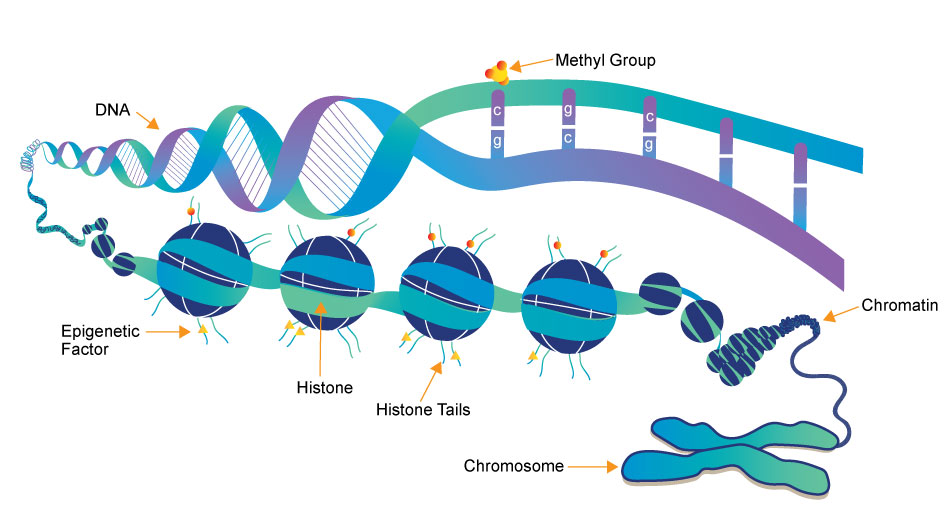

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
Aurora 抑制剂
Danusertib (PHA-739358) 是一种针对 Aurora A/B/C 的 Aurora 激酶抑制剂,在无细胞试验中的 IC50 分别为 13 nM/79 nM/61 nM,对 Abl、TrkA、c-RET 和 FGFR1 有适度的抑制效力,对 Lck、VEGFR2/3、c-Kit、CDK2 等的抑制效力较低。目前处于临床试验第二阶段。- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
-
multi-kinase 抑制剂
Cenisertib (AS-703569) 是一种多激酶抑制剂,能够阻断 Aurora-kinase-A/B、ABL1、AKT、STAT5 和 FLT3 的活性。 -
BCR-ABL 抑制剂
AP24534(Ponatinib)是一种强效的多激酶和全谱BCR-ABL抑制剂。- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
- Yamamoto Y, .et al. , Anal Biochem, 2019, Feb 13. pii: S0003-2697(18)31083-2 PMID: 30771339
- N Naganna, .et al. , EBioMedicine, 2019, Jan 24. pii: S2352-3964(19)30012-X PMID: 30686755
- Takuya Hirao, .et al. , Cancer Sci, 2018, Jan; 109(1): 121-131 PMID: 29121435
- Brittany M. Duggan, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 1578 PMID: 28484277
- Fujita KI, .et al. , J Pharm Sci, 2017, Sep;106(9):2632-2641 PMID: 28479358
-
Src/Abl 抑制剂
Saracatinib (AZD0530) 是一种高度选择性的、可口服的双特异性 Src/Abl 激酶抑制剂,其对 c-Src 和 Abl 激酶的 IC50 分别为 2.7 nM 和 30 nM。- Andromachi Lambrianidou, .et al. , Cell Signal, 2021, Apr;80:109912 PMID: 33388443
- Chisato Naito, .et al. , Atherosclerosis, 2016, Mar;246:344-51 PMID: 26828753
- Kenta Maruyama, .et al. , J Biol Chem, 2015, Apr 10; 290(15): 9377-9386 PMID: 25691576
- Amanda L Jackson, .et al. , Expert Opin Emerg Drugs, 2015, Jun;20(2):331-46 PMID: 26001052
-
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
Bafetinib (INNO-406) 是一种针对白血病潜在治疗的双重 Bcr-Abl/Lyn 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂。- Yusuke Kimata, .et al. , Life Sci Alliance, 2023, Feb 27;6(5):e202201657 PMID: 36849250
- Li T, .et al. , Oncogene, 2018, Nov;37(47):6180-6194 PMID: 30013190
- S. Dallari, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 14830 PMID: 28368000
- Andrea Haerzschel, .et al. , Ann Hematol, 2016, 95(12): 1979-1988 PMID: 27542958
- Magdalena Winiarska, .et al. , MAbs., 2014, 6(5): 1300-1313 PMID: 25517315
-
PDGFR 抑制剂
Imatinib (Gleevec) 是一种针对酪氨酸激酶酶的特异性抑制剂。- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
- Takafumi Shima, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2022, 47: 7 PMID: 34738628
- Reiko Watanabe, .et al. , J Med Chem, 2021, Mar 11;64(5):2725-2738 PMID: 33619967
- BM Duggan, .et al. , Endocrinology, 2020, May 30;bqaa086 PMID: 32473019
- Li Li, .et al. , Leukemia Res, 2019, 78:12-20 PMID: 30660961
- Brittany M. Duggan, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 1578 PMID: 28484277
-
Abl-Src 抑制剂
Dasatinib(BMS-354825)是一种口服多效 BCR/ABL 和 Src 家族酪氨酸激酶抑制剂。Dasatinib 的主要靶点包括 BCR/ABL、Src、c-Kit、ephrin 受体以及其他几种酪氨酸激酶,但不包括 erbB 激酶,如 EGFR 或 Her2。- Hiroyasu Aoki, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2024, Mar 26;43(3):113887 PMID: 38458195
- Hiroto Kataoka, .et al. , Anal Biochem, 2023, Oct 1;678 PMID: 37541642
- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
- Chihiro Motozono, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2022, Sep 21;13(1):5440 PMID: 36130929
- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
- Adi Jacob Berger, .et al. , Nat Cancer, 2021, 2, 1055-1070 PMID: 35121883
- David E J Klawon, .et al. , J Exp Med, 2021, Jun 7;218(6) PMID: 33914024
- Reiko Watanabe, .et al. , J Med Chem, 2021, Mar 11;64(5):2725-2738 PMID: 33619967
- Li Li, .et al. , Leukemia Res, 2019, 78:12-20 PMID: 30660961
- Sano T, .et al. , Am J Pathol, 2018, Nov;188(11):2564-2573 PMID: 30121259
- Ines Peschel, .et al. , Haematologica, 2017, Aug; 102(8): 1378-1389 PMID: 28522571
- Brittany M. Duggan, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 1578 PMID: 28484277
- John D. Leonard, .et al. , Immunity, 2017, Jul 18; 47(1): 107-117.e8 PMID: 28709804
- Fujita KI, .et al. , J Pharm Sci, 2017, Sep;106(9):2632-2641 PMID: 28479358
-
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
伊马替尼甲磺酸盐是一种选择性酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,通过抑制KIT信号传导途径,在治疗胃肠间质瘤中诱导了持续的客观反应。- Inge Govaerts, .et al. , J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14: 97 PMID: 34167562
- Genevra Kuziel, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2020, Jul 28;12(8):E2083 PMID: 32731354
-
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
Nilotinib 是一种 Bcr-Abl 抑制剂,其 IC50 小于 30 nM。- Rami Shinnawi, .et al. , Stem Cell Reports, 2015, Oct 13; 5(4): 582-596 PMID: 26372632
- Tetsuya Saita, .et al. , Biol Pharm Bull. , 2015, 38(10):1652-7 PMID: 26424026
-
EphB4 抑制剂
NVP-BHG712 是一种选择性的 EphB4 激酶 抑制剂,在体外对 EphB4 的选择性优于40多种其他激酶,包括 FGFR3。- Ryuzaburo Yuki, .et al. , Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, Jan 15:963:176229 PMID: 38072041
- Y Kaibori, .et al. , the FASEB Journal, 2019, Jan 22:fj201801519RR PMID: 30668924
-
DUB/Bcr/ABL 抑制剂
WP1130(Degrasyn)是一种新型选择性小分子去泛素化酶抑制剂,同时也是一种Bcr/Abl降解途径激活剂,能够特异性且迅速地降低慢性髓性白血病(CML)细胞中野生型和突变型Bcr/Abl蛋白的表达,而不影响bcr/abl基因的表达。- Kevin Bohm, .et al. , Arch Pharm (Weinheim), 2023, Jul;356(7):e2200661 PMID: 37196427
-
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
DCC-2036 是一种口服生物利用度高的小分子抑制剂,能够抑制多种酪氨酸激酶,具有潜在的抗肿瘤活性。- Hirosumi Tamura, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2018, Aug; 40(2): 635-646 PMID: 29917168
-
ABL/c-KIT dual kinase 抑制剂
CHMFL-ABL/KIT-155(CHMFL-ABL-KIT-155;化合物34)是一种高效的口服 II型 ABL/c-KIT 双重激酶抑制剂。 -
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
PD-173955 是一种 src酪氨酸激酶抑制剂。PD173955 抑制了依赖 Bcr-Abl 的细胞生长。PD173955 在 G(1) 阶段引起细胞周期阻滞。PD173955 在 Bcr-Abl 的激酶抑制测定中具有 IC(50) 值为 1-2 nM,并且在细胞生长测定中,它抑制了依赖 Bcr-Abl 的底物酪氨酸磷酸化。PD173955 抑制了依赖 kit 配体的 c-kit 自磷酸化(IC(50) = 约 25 nM)和依赖 kit 配体的 M07e 细胞增殖(IC(50) = 40 nM),但对依赖白细胞介素 3(IC(50) = 250 nM)或粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(IC(50) = 1 微米)的细胞生长影响较小。 -
BCR-ABL 抑制剂
CHMFL-ABL-039 是一种 II型原生ABL激酶 和 耐药性V299L突变BCR-ABL抑制剂,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为7.9 nM和27.9 nM。CHMFL-ABL-039 用于慢性髓性白血病的研究。 -
c-Abl/c-Kit/PDGRFβ 抑制剂
Flumatinib mesylate 可以在时间和剂量依赖的方式下降低 U266 细胞系中 C-MYC、HIF-1α 和 VEGF 的表达,因此 flumatinib mesylate 可能成为治疗多发性骨髓瘤(MM)的新药。 -
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
NRC-AN-019 是一种口服酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKI),针对 Bcr-Abl 蛋白酪氨酸激酶。NRC-AN-019 在抑制血管生成潜力和 MDAMB231 以及 HTB20/BT474 细胞的增殖方面更为有效。 -
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
Nilotinib 是一种 Bcr-Abl 抑制剂,其 IC50 小于 30 nM。 -
Bcr-Abl 抑制剂
GZD824 是一种新型的口服生物利用度 Bcr-Abl 抑制剂,针对 Bcr-Abl(WT) 和 Bcr-Abl(T315I),其 IC50 分别为 0.34 nM 和 0.68 nM。 -
multi-kinase 抑制剂
Flumatinib 是一种多激酶抑制剂,其 IC50 值分别针对 c-Abl、PDGFRbeta 和 c-Kit 为 1.2 nM、307.6 nM 和 2662 nM。 -
ABL 抑制剂
SNIPER(ABL)-062,其中一个ABL抑制剂通过含有可变聚乙二醇(PEG)单元的连接体与cIAP1的配体连接,显示出强大的活性以降解BCR-ABL蛋白。 -
ABL2 抑制剂
CHMFL-ABL-121 是一种高效的 II型 ABL激酶抑制剂,其对纯化的非活性 ABL wt 和 T315I 激酶蛋白的 IC50 分别为 2 nM 和 0.2 nM。 -
BCR-ABL 抑制剂
BCR-ABL-IN-2 是一种 BCR-ABL1 酪氨酸激酶 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 57 nM 和 773 nM,针对 ABL1native 和 ABL1T315I。 -
Src/c-Abl 抑制剂
1-萘基PP1盐酸盐是一种选择性抑制剂,主要针对src家族激酶v-Src和c-Fyn以及酪氨酸激酶c-Abl(IC50值分别为v-Src 1.0 μM、c-Fyn 0.6 μM、c-Abl 0.6 μM、CDK2 18 μM和CAMK II 22 μM)。 -
Bcr-Abl1 抑制剂
Vodobatinib,也被称为 K-0706,是一种新型的第三代(3G)TKI,对野生型和突变型 BCR-ABL1 有效,且具有有限的非靶点活性。 -
multi-kinase 抑制剂
多激酶抑制剂1是一种强效的多激酶抑制剂。多激酶抑制剂1具有治疗与异常或失调的酪氨酸激酶活性相关的疾病或疾患的潜力,特别是与PDGF-R、c-Kit 和 Bcr-abl 活性相关的疾病。